a form of positional behavior (i.e., posture and locomotion) that utilizes only the hind limbs; an animal that locomotes on two legs is referred to as a biped. See also facultative bipedalism and habitual bipedalism.
a stone tool with a length that is twice its width; usually hafted into bone or wooden implements.
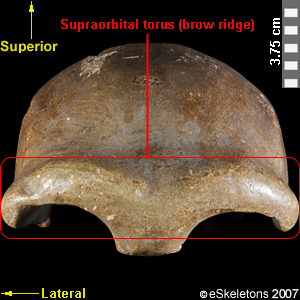
[syn. supraorbital torus] the bony protrusion above the eye orbit seen in many primates. The brow ridge is very pronounced in Archaic Homo sapiens (i.e., H. heidelbergensis) and H. neanderthalensis.
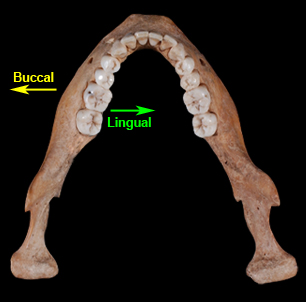
term used for elements in the mouth closest to the cheek.
premolars and molars that have low, rounded cusps.
eFossils is a collaborative website in which users can explore important fossil localities and browse the fossil digital library. If you have any problems using this site or have any other questions, please feel free to contact us.
Funding for eFossils was provided by the Longhorn Innovation Fund for Technology (LIFT) Award from the Research & Educational Technology Committee (R&E) of the IT governance structure at The University of Texas at Austin.
