Read about "Ardi". Ardipithecus ramidus, discovered in 1994, may be one of the oldest known hominins in the family tree. Image by T. Michael Keesey.
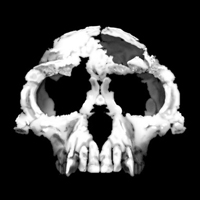
Read about "Ardi". Ardipithecus ramidus, discovered in 1994, may be one of the oldest known hominins in the family tree. Image by T. Michael Keesey.

The newly discovered Australopithecus sediba lived in South Africa between 1.75 and 1.95 million years ago. Read the article. Photo by Brett Eloff.
From a finger bone and a molar, researchers have mapped the genome of newly discovered extinct hominins who lived 30,000 years ago. View the results here.
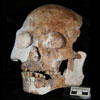
Descriptions of fossils from Southwest China have sparked new debate about human evolution in Asia. Photo by Darren Cunroe (via LiveScience).
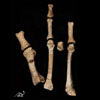
Foot bones from Burtele suggest a hominin with an opposable big toe lived in Ethiopia 3.4 Ma. Image ©The Cleveland Museum of Natural History via LiveScience.
Watch a discussion about the survival of the human species when other hominins have gone extinct. Recorded at the World Science Festival in New York on June 2.
Analysis of artifacts from Border Cave in South Africa suggest that the moder hunter-gather culture developed by 44 Ka. Read the PNAS article. Image by Werner Hammer.
3 August 2012: Volcanic ash analysis suggests intraspecies competition was a greater threat to Neanderthal survival than natural disasters or climate change.
15 Nov 2012: Read the Science report that suggests spear use may date back to an early ancestor who lived over 500 Ka.
13 Mar 2013: Neanderthals may have relied more heavily on sight than modern humans. Read more in Proceedings B.
3 Oct 2012: As reported in PLOS, signs of anemia in a recently discovered skull suggest meat was a dietary staple by at least 1.5 Ma.
26 Jun 2013: Baseball's fast ball may owe its success to a 2 million year old hunting technique - read about it in Nature.
25 Jul 2013: Reanalysis of the evidence suggests Oreopithecus (9-7 Ma) wasn't a habitual bipedal as previously claimed.
1 Aug 2013: An article in Science discusses a possible link between climate and the evolution of our early hominin ancestors.
2 Aug 2012: The human male genome may date back to between 120 Ka and 156 Ka, as reported in Science.
eFossils is a collaborative website in which users can explore important fossil localities and browse the fossil digital library. If you have any problems using this site or have any other questions, please feel free to contact us.
Funding for eFossils was provided by the Longhorn Innovation Fund for Technology (LIFT) Award from the Research & Educational Technology Committee (R&E) of the IT governance structure at The University of Texas at Austin.
